Introduction of the new era of smarter food safety
We are living in a time of fast global change, particularly with regard to food. As a result of change, the food industry is facing new challenges. Globalization, population increase, and climate change are a few of the issues posing a challenge to food safety regulations. Digitalization and innovative technology, however, can assist in addressing these issues by offering fresh resources and approaches.
The following article explores new technology-driven solutions for achieving food safety, and how food safety stakeholders are dealing with it. [1] [2]
What is Industry 4.0?
According to SSAFE, Industry 4.0 includes:
1. Connectivity: cloud-based systems, Internet of Things (loT), Big Data, blockchain.
2. Analytics: advanced analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence.
3. Human-machine interaction: augmented reality (AR), advanced robotics and automation.
4. Advanced engineering: additive manufacturing.
The Smarter Era Core Elements according to the FDA
In 2019, the New Era of Smarter Food Safety Initiative was launched by the FDA. Experts in the field cooperated to provide their vision about the future of food safety in relation to new smarter tools. According to the experts, these four elements, synergically working together, will bring us into the New Era of Smarter Food Safety. [2]
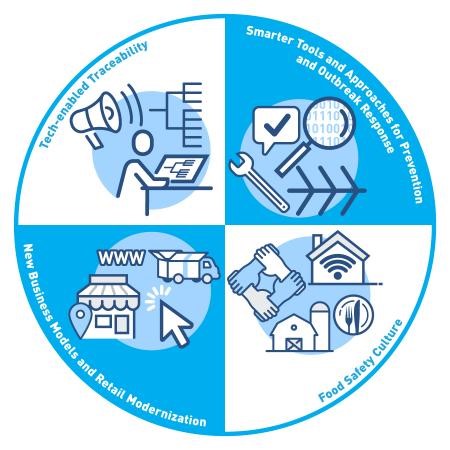
1. Tech Enabled Traceability
- The food industry still relies on paper-based records; this can result in delays when trying to rapidly track and trace food. Technology can provide faster tools, such as ways to identify outbreaks and trace the origin of contaminated food in minutes. Tech-enabled traceability is one of the fundamental pillars that support the variety of technologies. [2]
2. Smarter Tools and Approaches for Prevention and Outbreak Response
- More available data streams can be used for predictive analytics to better identify where contamination is likely to occur and prevent contaminated products from entering the market. [2]
3. New Business Models and Retail Modernization
- New business models are appearing in the food industry: especially after the pandemic, online grocery shopping became popular, and new food trends and novelty food are emerging. While these innovations can be positive, regulatory agents must provide support to ensure that the correct actions will be in place to avoid any food safety risks. [2]
If you want to know more about new customer trends and novelty food, read the following article.
4. Food Safety Culture
- Influencing and altering human behavior by focusing on how staff members view food safety and how they show dedication to this objective by carrying out their duties is of extreme importance. Food safety culture can be supported by using smarter tools, for instance by encouraging e-training or logged-in recording of actions of employees. [2]
Potential food safety benefits
According to SSAFE, the following could be the potential benefits of adopting innovative technologies for food safety management:
- Improving traceability and transparency capabilities
- Providing process assurance
- Boosting predictive capabilities for food safety
- Supporting continuous improvements in quality and food safety [1]
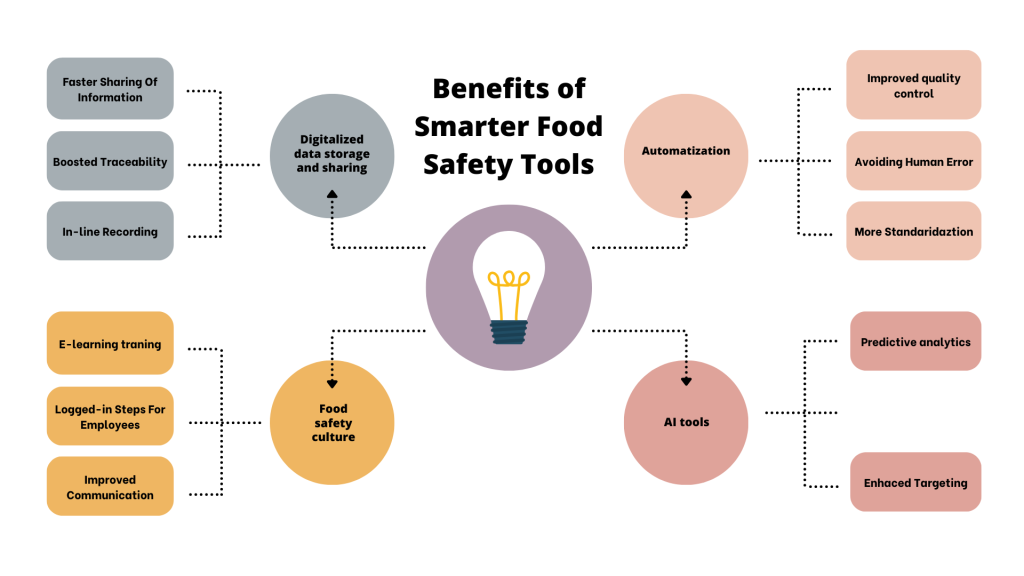
Adoption of Smarter Tools and Industry 4.0 by the food industry
The adoption of technologies in the food industry is still in the beginning and is estimated to be around 20% to 40% [1]. Smarter tools and Industry 4.0, though, have great potential to improve the food industry, especially in regard to food safety management. The SSAFE report on Industry 4.0 provides a list of examples of problems that the food industry is facing and practical solutions that could be applied to solve them.
Farming:
- Crops are at risk of being contaminated.
->Precision agriculture to detect contamination and reduce the use of pesticides. By use of drones and sensors to sense the traces of chemicals, and biological hazards. [1]
R&D and Procurement:
- Accessing information can be difficult because of paper-based documentation, and unstructured data. This ultimately impacts data sharing and trend analysis.
->Automating data collection would make sharing of data quicker. Data such as location and temperature can be collected in real-time. Furthermore, AI tools can be employed to predict food products and suppliers that are at risk. [1]
Processing/manufacturing:
- The food industry relies on manual labor, which is susceptible to human error.
-> Automated record-keeping would leverage standardization and reduce errors. Moreover, online monitoring and testing can be implemented and carried out in real-time and cover 100% of the samples. [1]
Distribution:
- Moving the products can expose them to potential hazards, such as temperature change, light or incorrect handling ultimately impacting food safety.
->Automated data collection, IoT sensors, and customer feedback monitoring can reduce the risk of such hazards happening or going unnoticed. [1]
Restaurants and Catering:
- Food service providers are the most common reason for exposure to foodborne illness.
-> By investing in a digitalized management of their stocks and expiration dates, hospitality services can greatly reduce the risk of introducing hazards. Furthermore, other monitoring practices can be put in place, such as digital interactive SOPs for employees. [1]
What are the potential drawbacks and limitations?
- Overreliance on technology
- Data privacy and security matters
- Lack of regulations and standardizations
- Costs [3] [2]
QAssurance Smarter Food Safety Solutions: iMIS Food Digitalization
The food industry is progressively becoming more technological and digitalized, and so is food safety management.
iMIS Food provides a real-time Food Safety system that helps food companies comply with all regulations, procedures, and GFSI food safety standards such as IFS, BRC, and FSSC 22000. Nevertheless, with the help of the system, food companies can easily embrace digitalization and move away from pen-and-paper practices.
Besides the tracking system, iMIS Food offers multiple digital solutions to aid food companies in complying with the latest legislation and standards, such as a digital handbook with all procedures and the HACCP study, an audit round system where hygiene, cleaning, product, or process checks can be performed and reported via smartphone, the intranet and portal, which offer access to the entire system, a calendar, as well as the documentation system.
iMIS digital solutions:
– iMIS Food Handbook
– iMIS Food Audit
– iMIS Speccheck
– iMIS Intranet
– iMIS Food Tracking
Food Safety Culture
As highlighted by the FDA blueprint “New Era of Smarter Food Safety” food safety culture will be imperative to the future of food safety management. IMIS Food provides companies with a Food Safety Culture Scan for staff. This tool makes food safety culture measurable among staff by completing a number of simple agree and disagree questions.
Sources
- [1] SSAFE. (2023). Industry 4.0 and Food Safety. In SSAFE.
- [2] FDA. (2023). New Era of Smarter Food Safety. In FDA.
- [3] Food safety gets smarter – IFT.org. (2021, April 1). https://www.ift.org/news-and-publications/food-technology-magazine/issues/2021/april/features/food-safety-gets-smarter
Related articles to The New Era of Smarter Food Safety
Many customers and visitors to this page 'The New Era of Smarter Food Safety' also viewed the articles and manuals listed below:



