Introduction
In an era of growing environmental consciousness, sustainability certifications have become essential tools for consumers and businesses in the food industry. These certifications act as a compass, guiding consumers toward products that align with their values and support responsible practices. From organic farming to fair trade and beyond, a wide array of certifications exists, each with its own specific standards and focus areas.
This article delves into the world of sustainability certifications, examining their benefits, challenges, and prospects.
Sustainability: A Foundation for the Future
Sustainability is about meeting present needs without jeopardizing the future. It’s a delicate balance between environmental protection, economic growth, and social fairness.
In the context of the food industry, sustainability entails producing and consuming food in a way that:
- Protects the environment: Minimizes the use of natural resources, reduces pollution and waste, and promotes biodiversity
- Supports economic viability: Ensures the long-term economic success of the industry while providing fair wages and opportunities for all stakeholders
- Promotes social equity: Respects the rights and well-being of workers, communities, and consumers
The Path to Sustainability and its Barriers
The food industry is at a crossroads. While sustainability is increasingly crucial to consumers, recent data suggests waning trust. This scepticism, fueled by concerns about greenwashing and distrust in the food industry (Figure 1), has created a gap between consumer ideals and the industry’s current performance.
However, the desire for sustainable food remains strong. A significant majority of consumers still strive to live sustainably, and environmental impact factors into their dietary choices. Bridging this trust gap is essential.
Companies must prioritize transparency, authenticity, and measurable results to regain consumer confidence. By demonstrating a genuine commitment to sustainability and communicating their efforts clearly, the industry can meet growing demands and create a food system that benefits both people and the planet. Sustainability isn’t just a trend; it’s a defining factor for the future.

Key Sustainability Certifications in the Food Industry
In today’s world, where environmental and ethical concerns are increasingly influencing our purchasing decisions, sustainability certifications have emerged as valuable tools for navigating the marketplace. But what exactly are these certifications, and how can they empower consumers to make informed choices?
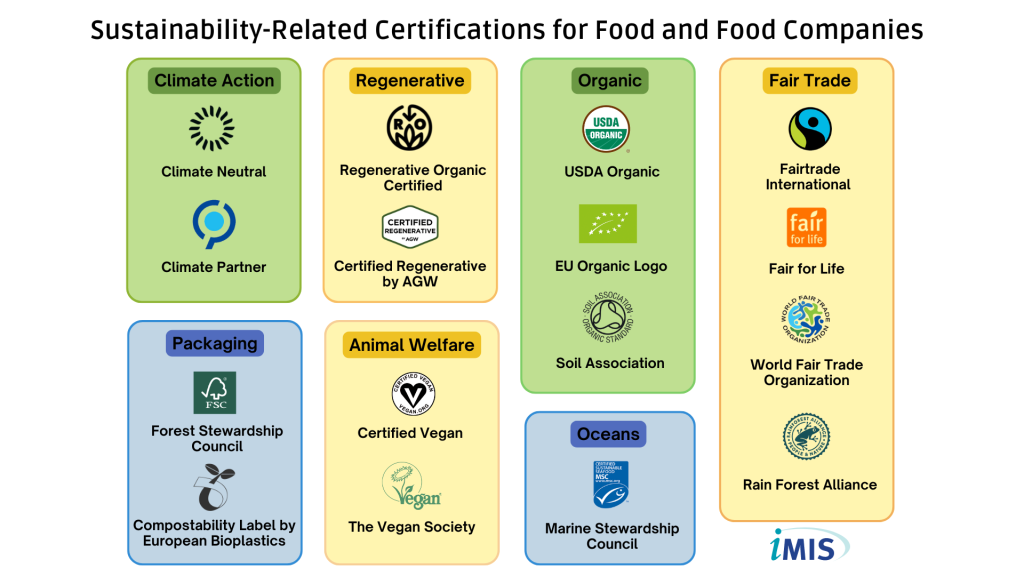
Sustainability certifications are essentially third-party endorsements that verify a product or service meets specific environmental, social, or ethical standards. These standards can encompass a wide range of issues, from reducing carbon emissions and protecting biodiversity to ensuring fair labour practices and supporting local communities (Figure 2).
By opting for certified products, consumers can actively contribute to a more sustainable and equitable world. Certifications offer a tangible way to align our values with our purchasing power, fostering a sense of agency and responsibility.
Key Sustainability Certifications at a Glance:
- Climate Action: Recognizes efforts to cut greenhouse gas emissions
- Regenerative Agriculture: Goes beyond sustainability, focusing on practices that actively restore ecosystems and boost biodiversity
- Organic: Prohibits synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and GMOs, promoting soil health and animal welfare
- Fair Trade: Ensures fair prices and working conditions for farmers and workers, supporting sustainable agriculture
- Packaging: Evaluates packaging materials based on recyclability, composability, and reduced environmental impact
- Animal Welfare: Guarantees animals are raised humanely with proper care, shelter, and space
- Oceans: Ensures seafood comes from sustainable fisheries, minimizing impact on marine life
The Benefits of Sustainability Certifications
Sustainability certifications play a pivotal role in fostering a more transparent and responsible food system. They offer a multitude of benefits for both consumers and producers, driving positive change in the industry:
- Consumer Trust: Certifications boost confidence in consumers, assuring them that the products they choose align with their values and support sustainable practices
- Market Access: For producers, certifications can unlock new markets and create opportunities for premium pricing, recognizing their commitment to sustainability
- Improved Practices: The certification process often encourages continuous improvement in environmental and social performance, pushing companies to adopt more sustainable practices
- Brand Reputation: By obtaining certifications, businesses demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, enhancing their brand reputation and attracting conscious consumers
Challenges and Considerations
While certifications serve as valuable guides, it’s crucial to approach them with a discerning eye. Several challenges and considerations can influence their effectiveness:
- Cost and Complexity: The certification process itself can be time-consuming and expensive, particularly for smaller producers. This can create a barrier to entry, limiting the availability of certified products
- Certification Proliferation: The sheer number of different certifications can be overwhelming, leading to confusion for both consumers and businesses
- Greenwashing Concerns: Some companies may engage in “greenwashing” – making misleading sustainability claims without proper certification. It’s essential to be vigilant and research certifications thoroughly to ensure their legitimacy
The Future of Sustainability Certifications: Anticipating Change
The increasing consumer demand for sustainable food is driving a wave of change across the food industry, influencing standards, regulations, and even how companies operate. In the EU, initiatives like the Farm to Fork strategy are spearheading this transformation. The European Parliament is actively combating greenwashing by pushing for standardized labelling, with the potential expansion of the Ecolabel to food products on the horizon.
Furthermore, emerging technologies like blockchain and AI will further amplify transparency and traceability, empowering consumers with verifiable information.
To thrive in this evolving landscape, companies must proactively embrace change. Communicating transparently, investing in technology for tracking sustainability, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement is essential. Collaboration with stakeholders and industry partners will be key to building a truly sustainable food system.
Conclusion
The journey toward a sustainable food system requires collective effort from consumers, producers, and regulators. Sustainability certifications serve as crucial signposts on this path, guiding us toward a future where food production and consumption are in harmony with the planet and its inhabitants.
As consumer demand for sustainable food continues to grow, it is imperative for the food industry to embrace transparency, innovation, and collaboration. By prioritizing sustainability and actively communicating their efforts, businesses can not only meet the evolving demands of consumers but also play a vital role in shaping a more equitable and resilient food system for generations to come.
Sources
- [1] Dhanani, R. (2024, September 9). A guide to sustainabilitycertifications. The Sustainable Agency. https://thesustainableagency.com/blog/sustainability-certifications-and-ecolabels-guide/
- [2] Eating sustainably – easier than you think? (2022, July 28). European Climate Pact. https://climate-pact.europa.eu/news-and-events/pact-articles/eating-sustainably-easier-you-think-2022-07-28_en#:~:text=is%20critically%20important.-,People%20are%20increasingly%20aware%20that%2C%20when%20it%20comes%20to%20food,is%20good%20for%20them%20too
- [3] Fewer consumers report making healthy and sustainable food choices, reveals pan-European study – EIT Food. (n.d.). EIT Food. https://www.eitfood.eu/news/fewer-consumers-report-making-healthy-and-sustainable-food-choices
- [4] Innova Market Insights. (2024, July 8). European Consumer Trends: Sustain ability and Ethics. https://www.innovamarketinsights.com/trends/european-consumer-trends-sustainability/
- [5] Nygaard, A. (2023). Is sustainable certification’s ability to combat greenwashing trustworthy? Frontiers in Sustain ability, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/frsus.2023.1188069
- [6] Stewart, B. (2023, June 30). How Product Certification Can Help Consumers Make More Sustainable Choices during Tough Economic Times – GlobeScan. https://globescan.com/2023/06/29/how-product-certification-can-help-consumers-make-more-sustainable-choices-during-tough-economic-times/#:~:text=The%20impact%20that%20a%20Fairtrade,certifications%20are%20to%20consumers%20in
- [7] Sustainable food. (n.d.). RIVM. https://www.rivm.nl/en/food-and-nutrition/sustainable-food#:~:text=Sustainable%20food%20is%20defined%20as,both%20environmentally%20friendly%20and%20healthy.
Related articles to Navigating the World of Sustainability Certification in the Food Industry
Many customers and visitors to this page 'Navigating the World of Sustainability Certification in the Food Industry' also viewed the articles and manuals listed below:
