Food Safety certifications
This graph shows the number of Food Safety certifications (IFS, FSSC22000 and BRC) in Africa, Latin America, Germany, Italy and India. As it can be seen, Italy leads with more than 7 thousand certifications followed up by Germany with around 6 thousand, while India has approximately 2 and a half thousand. Latin America registers 4 thousand certifications whereas Africa has a bit more than India. Italy alone has more than twice the number of certifications compared to Africa. In order to understand the gaps in numbers figure 1 illustrates how big Italy (green) is in comparison with Africa.
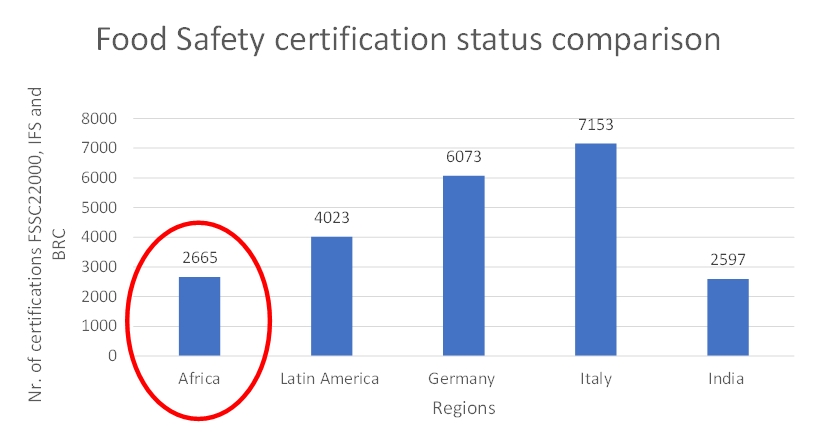
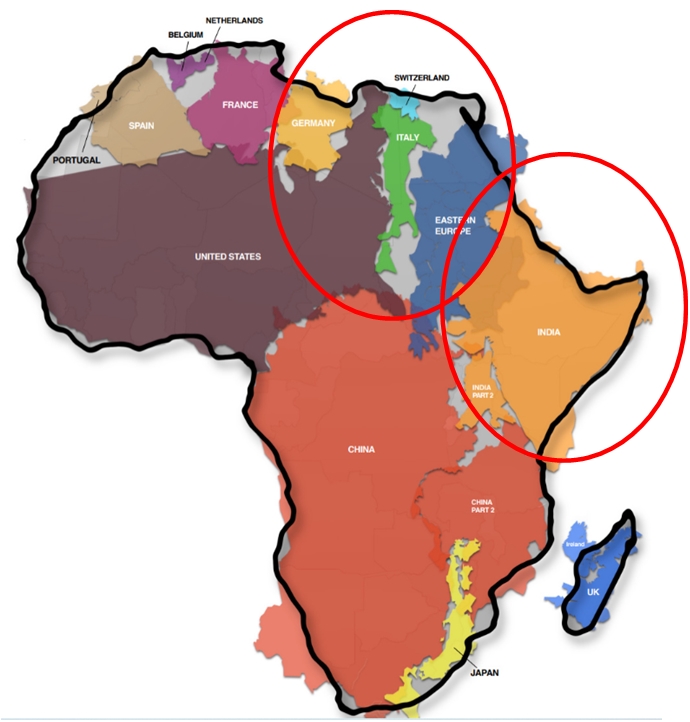
Figure 1: Land comparison of regions
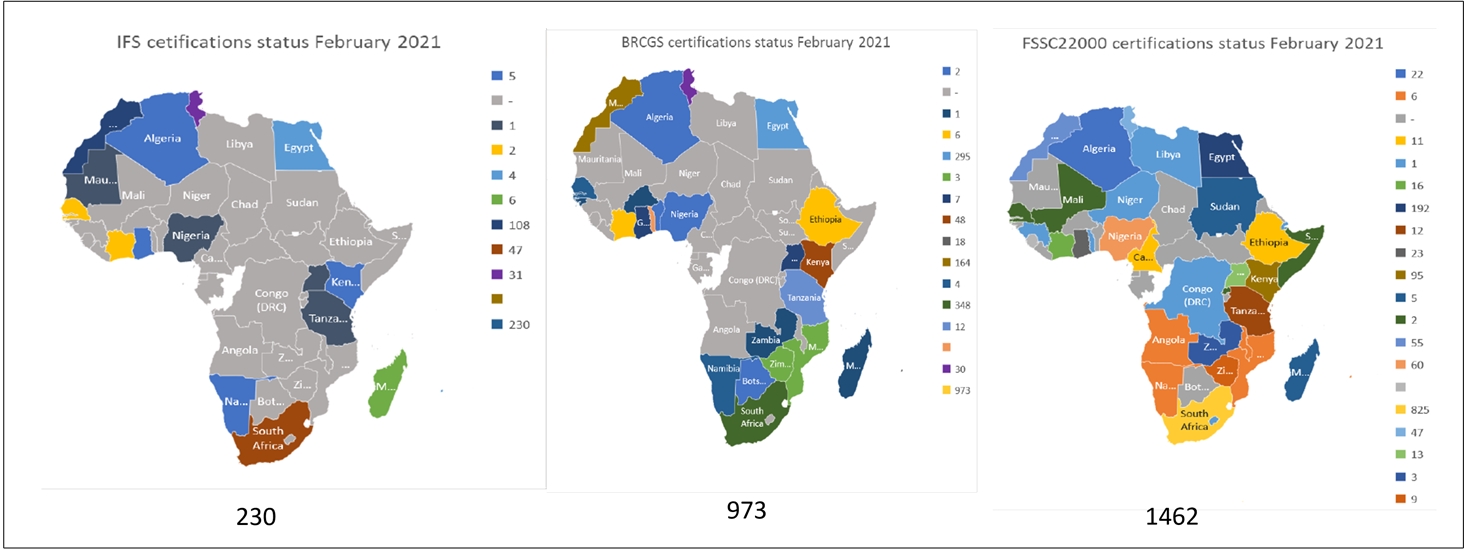
Figure 2: Food Safety certification status in Africa in 2021. (Sources: IFS, BRC, FSSC22000)
Why has Africa lagged behind?
Firstly, Africa lacks food safety management capacity (Jaffee, 2020) which refers to:
- human capital (basic knowledge, specialized expertise, management, leadership as well as communication skills)
- physical infrastructure (safe storage, cold chain, sanitary facilities, processing equipment and laboratory capacity)
- management systems (enterprises, regulatory agencies, laboratories).
Assessments have been undertaken by WHO to evaluate the capacity within Africa based on indicators for food safety. The findings can be seen in figure 3.
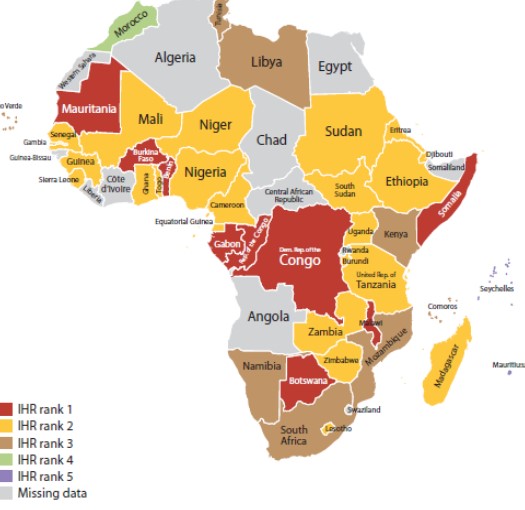
Figure 3: Capacity ranking on food safety indicators according to WHO in Africa. (Source: Jaffee, 2020)
This study shows a five-point scale where (1) indicates no capacity whereas (5) shows sustainable capacity. Out of the 47 countries assessed most of them registered low scores between 1 and 2, meaning there is a lack of capacity. Only Seychelles scored the highest rank for food safety, while Mauritius and Morocco received a score of 4. (Jaffee et al., 2020)
Secondly, there is a lack of information regarding the importance of Food Safety and motivation for compliance due to political instability, diseases, natural catastrophes, corruption, food insecurities and other factors that are primordial to African governments. Therefore, the correct holistic approach to food safety could not be adopted. Furthermore, there is a deficiency in knowledge and expertise. Several Food Safety authorities were unable to enforce the legislation due to a lack of international regulations (CODEX) or inspection mechanisms (expertise and physical infrastructures) in most countries. In many African countries, the implementation of HACCP in food production companies is not applied as the majority are informal small and medium enterprises (SMEs) that operate outside of Food Safety regulations or any formal system. (Oloo et al.,2018)
Nonetheless, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasing as the urbanization trend is growing and the middle class is forming. The retailers ask for high-quality and safe food, hence they put pressure on SMEs and seek producers who are able to meet food safety standards. However, the smallholders and SMEs cannot afford the high cost of compliance and thus are dominated by larger players and by the two-tier system with safe and high-quality food for export and lower standards for the domestic informal market. (Manning et al., 2019, Whitworth, 2021)
Therefore, information regarding the importance of Food Safety is crucial as well as knowledge on Food Safety compliance. Likewise, investments in Food Safety management capacity are critical in order to apply this understanding. Yet, changes have been registered and the urge to improve has been seen. The African Union Commission is working towards regional harmonization of regulatory standards in the Regional Economic Communities (RECs) as well as capacity building. Moreover, many African nations are designing new legislations and regulations which better reflect the food safety needs. (GFSP, 2019; Oloo et al., 2019)
iMIS Food Global enhances Food Safety and works toward food security
Emerging countries with poor infrastructure and weak food legislation frameworks can benefit from private standards in terms of designing and implementing food safety management systems. Furthermore, the compliance with private standards in these countries creates and facilitates access to global markets. (Manning et.al, 2019) However, it can be argued that smallholders and SMEs cannot afford to comply with these standards due to high financial costs and a lack of knowledge. (Manning et al., 2019, Oloo et al., 2019; GFSP, 2019)
Importance of certification:
- Access to regional and global markets
- HACCP implementation
- FSMS implementation
- Less food loss due to quality system
”There is no food security without food safety.” (FAO, 2019)
Food Safety is embedded in Food Security. (GSP 2019, FAO, 2019) Food Safety threats cause loss of food and thus waste of natural resources. (FAO, 2019)
Furthermore, Food Safety is directly linked to achieving many SDGs such as SDG 1 (end poverty), SDG 2 (end hunger), SDG 3 (good health and well-being), as well as it contributes indirectly to SDG 5 (gender equality), SDG 8 (decent work and economic growth) and SDG 11 (sustainable cities and communities). (Jaffee et al., 2019) Hence, sustainability was addressed by QAssurance. QAssurance wants to enhance Food Safety in African emerging countries through iMIS Food Global Implementation and Food Export Program.
Firstly, the implementation of iMIS Food Global in African emerging countries will have an environmental impact. Food loss and waste will be mitigated through proper quality management. Improving Food Safety and quality along the supply chain yields fewer losses in terms of food and natural resources. Secondly, the food supply will benefit from access to global markets and trade. Lastly, it will address some social aspects by improving nutrition and health amongst people by ensuring safe and high-quality food products in the agri-food chains. Read more about our Food Export Program
Sources
FAO (2019), The future of food safety. There is no food security without food safety.
Jaffee, S.; Henson, S.; Grace, D.; Ambrosio, M.; and Berthe, F., (2020). Why food safety matters to Africa: Making the case for policy action. In 2020 Annual trends and outlook report: Sustaining Africa’s agrifood system transformation: The role of public policies. Resnick, Danielle; Diao, Xinshen; and Tadesse, Getaw (Eds). Chapter 10, Pp. 112-129. Washington, DC, and Kigali: International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) and AKADEMIYA2063. https://doi.org/10.2499/9780896293946_10
Manning, L., Luning, P.A., Wallance, C.A., (2019), The evolution and cultural framing of food safety management systems – where from and where next? In: Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety. 00,2019. Institute of Food Technologists. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12484
Oloo, B., Daisy, L., Oniang’o, R., (2018), Food Safety legislation in some developing countries. In: Food Safety – Some Global Trends. DOI:10.5772/intechopen.75587
GFSP (2019), Food Safety in Africa: Past Endeavors and Future Directions. Appendix E Country activities in food safety [Online available at] https://files.constantcontact.com/d83c7c0d401/084bf2f0-9297-4996-8a15-b956a5f978b3.pdf
Whitworth, J., (2021), IFC highlights challenges for domestic food safety in Africa. In: Food Safety News. [Online available at] https://www.foodsafetynews.com/2021/05/ifc-highlights-challenges-for-domestic-food-safety-in-africa/
Related articles to Food Safety certification status in African countries
Many customers and visitors to this page 'Food Safety certification status in African countries' also viewed the articles and manuals listed below:
