Introduction
Food is an essential commodity. Despite this, it is estimated by the World Health Organization that eating food that is processed by others will result in a foodborne illness in 1 to 10 people. Furthermore, an increasingly complex food delivery system makes food safety management progressively more challenging. Many food safety authorities worldwide are promoting the concept of food safety culture, to advocate for better safety management systems. [5]
What is food safety culture and why is it important
The GFSI defines food safety culture as “shared values, beliefs and norms that affect mindset and behavior toward food safety in, across and throughout an organization.” In this context, people are seen as the most important aspect of food safety management. In fact, employees behavior and behaviors, from farm procedures to customer service, contribute to food safety and may reduce or increase the risk of foodborne illness. [5]
The most important reasons why food safety culture is so important:
- Prevention of foodborne illnesses
- Recall prevention
- Shared sense of responsibility
- More trust from consumers [5]
To address the importance of food safety culture, the GFSI released a guidance report that highlights all steps of food safety culture within a company. Read a summary here.
How is food safety culture created?
According to a literature review on food safety culture conducted by the FDA [4], the key factors for a proper establishment of food safety culture within a company are:
1. Leadership
Leaders have the authority to determine what is critical to the organization and can motivate the staff to change. [4]
2. Communication
Organizations with a strong food safety culture have a defined food safety communication strategy and involve employees at all levels. [4] Good communication examples include:
- Sharing data that is representative.
- Storytelling [2]
3. Commitment to food safety
The extent to which the organization is prioritizing food safety. [4]
4. Risk awareness
The understanding of all employees of the potential hazards associated with food safety. Food safety is a positive result of a corporation successfully managing all hazards to food safety. Thus, when the dangers are eliminated or reduced, the guarantee of the food’s safety increases tremendously. [2]
5. Environment
Organizational structures are in place to maintain proper food safety. Examples include equipment, staff, and training. [4]
6. Accountability
Employees at all levels must be held accountable for food safety. Expectations for food safety should be clear, risk-based, and relevant. [2] It is particularly successful the method of “rewards and recognition programs” which aims to reinforce positive food safety behaviors among employees.
The benefits of reward and recognition programs are:
- Engaging employees.
- Building trust
- Addressing social motivators [4]
7. Employees characteristics
Employee characteristics such as knowledge, attitude, behavior, and values can all impact food safety culture. [4] Employees who value food safety can positively influence others. This can be achieved by building food safety coalitions and food safety champions among employees. [2]
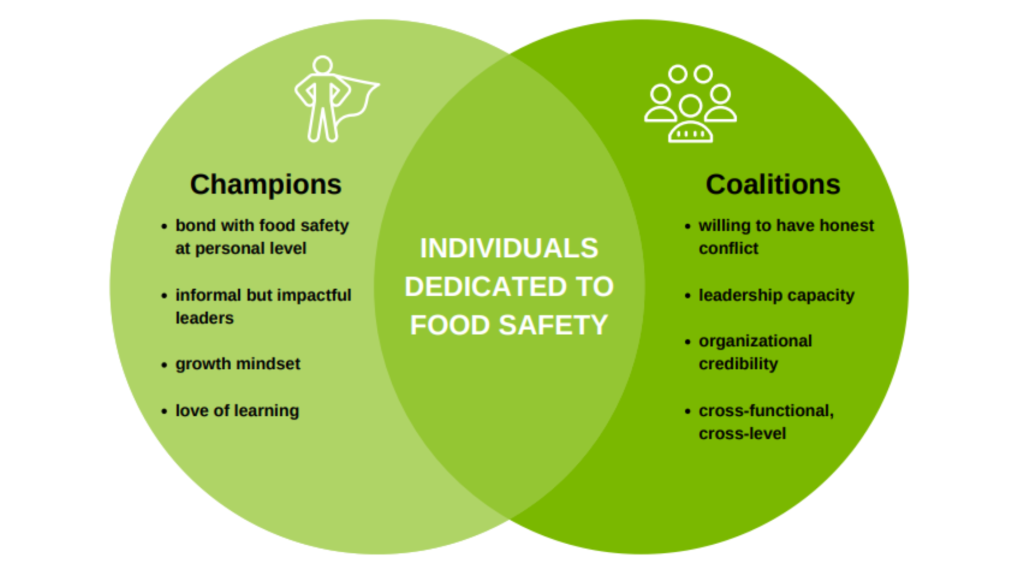
Training, learning, and education for food safety culture
The most important aspect in the building of a strong food safety culture is effective training programs. Training programs can be of various nature but should include all levels of employees.
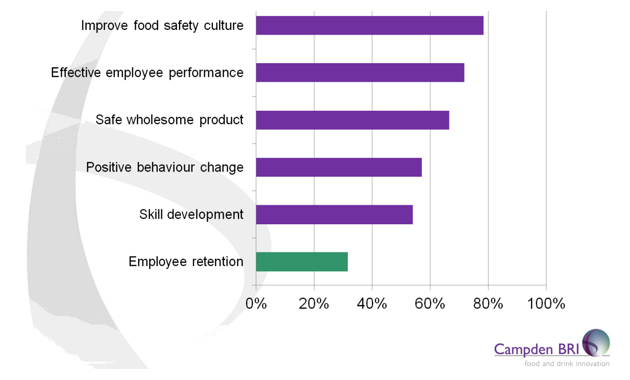
In 2016, Campden BRI released a global survey on food safety training. [1] Results revealed interesting insights (see Figure 2):
- Improvement of food safety was the 1st goal of 80% of the surveyed.
- Food safety culture was one of the top benefits of training.
Yet ->
- Less than 50% included food safety culture in their training program.
- Only 35% measured levels of food safety culture.
- Only 19% included food safety culture in their food safety audits. [1]
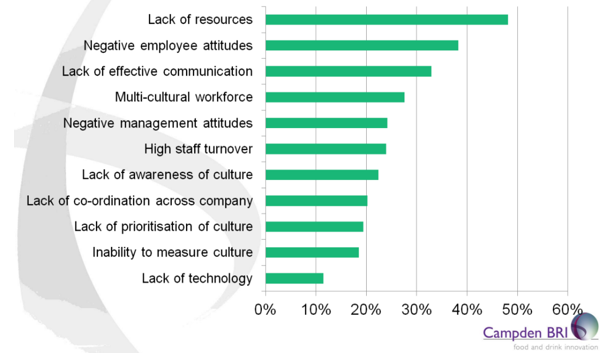
Challenges of creating a strong food safety culture
Despite the importance of boosting food safety culture within a company, it can be challenging. The Campden BRI survey on food safety training pointed out some of the most common challenges that can be faced in the process of building a food safety culture. [1,6] Possibly, the latest technologies introduced in the food safety management deal, could ease dealing with some of these challenges, for instance by creating a more digitalized and accessible data sharing [3]. More data accessibility could partially resolve the issue of lack of resources, which, in 2016, was outed as the biggest challenge in developing a strong food safety culture.
Assessing food safety culture in a company
- Performance measurement enables monitoring in line with stated food safety policies, expectations, and standards, as well as recognizing good performance and making improvements when necessary.
- Results should be clear and communicated within the organization.
Examples of ways to monitor food safety culture include surveys, questionnaires, and internal and external audits. [4]
Digitalization as a tool for food safety culture
In 2016, the Campden BRI survey on training found that traditional training methods were still preferred compared to online methods. [1]
Luckily, this is changing. The importance of food safety culture has been highlighted in the FDA blueprint “New Era of Smarter Food Safety” whose focal point is the future of food safety in relation to smart technologies. The paper emphasizes how food safety culture should be promoted in the future industry and offers examples of digitalized ways to do it. Examples include online training, digitalized feedback, social media, and logged-in monitoring of employees’ actions. [3]
To read more about smarter tools for food safety, read this article on smarter tools for food safety management.
Training with QAssurance
Awareness of food safety issues and hazards can be a complicated matter, especially beyond the quality department. However, food safety is a team effort. Therefore, there should be capacity, time, and skill to teach each department the basics of food safety.
QAssurance offers multiple trainings:
Food Safety Culture Scan
QAssurance offers the iMIS Food Safety Culture scan based on the 7S model, which is used more often in organizational science and business transformation. When getting the results, we do not just look at the scores, but also at where the biggest differences are. If departments have a completely different perspective, then it is good if you can map it out and, when necessary, start the conversation to see where there is room for improvement. The scan is fast, and a report of the results will be generated directly.
Sources
- [1] Campden BRI. (2016). Global Food Safety Training Survey 2016. In Campden BRI.
- [2] Collaborating on culture in the new era of smarter food safety. (2023, October 5). U.S. Food And Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/food/workshops-meetings-webinars-food-and-dietary-supplements/collaborating-culture-new-era-smarter-food-safety-12062023
- [3] FDA. (2020). New Era of Smarter Food Safety.
- [4] FDA. (2022). Food Safety Culture Systematic Literature Review.
- [5] GFSI. (2018). A culture of food safety: A position paper from the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI). In GFSI.
- [6] Global food safety training survey 2016 at Campden BRI. (n.d.). https://www.campdenbri.co.uk/pr/global-food-safety-training-survey.php
Related articles to The importance of food safety culture
Many customers and visitors to this page 'The importance of food safety culture' also viewed the articles and manuals listed below:
