From perfectly plated dishes to mouthwatering recipe tutorials, social media has become an undeniable force shaping our relationship with food. While platforms like TikTok and Instagram can be valuable tools for sharing and gaining information about safe food handling practices [3], they can also facilitate the rapid spread of false or misleading information, potentially leading to harmful practices [9].
This article unravels the complex relationship between social media and food safety, exploring how digital platforms influence perceptions and practices. By understanding the nuances of this digital landscape, food safety experts and consumers alike can gain valuable insights and strategies for responsibly navigating the abundance of online information.
How Social Media Promote Food Safety
Digital platforms have transformed how we access and share information, and food safety is no exception. With real-time updates, personal anecdotes, and engaging discussions at their fingertips, individuals are increasingly turning to social media for guidance on safe food handling practices. The widespread adoption of these platforms is evident in a 2021 USDA survey, which revealed that 82% of state food safety agencies utilize social media for both general communication and recall announcements (Figure 1) [8].
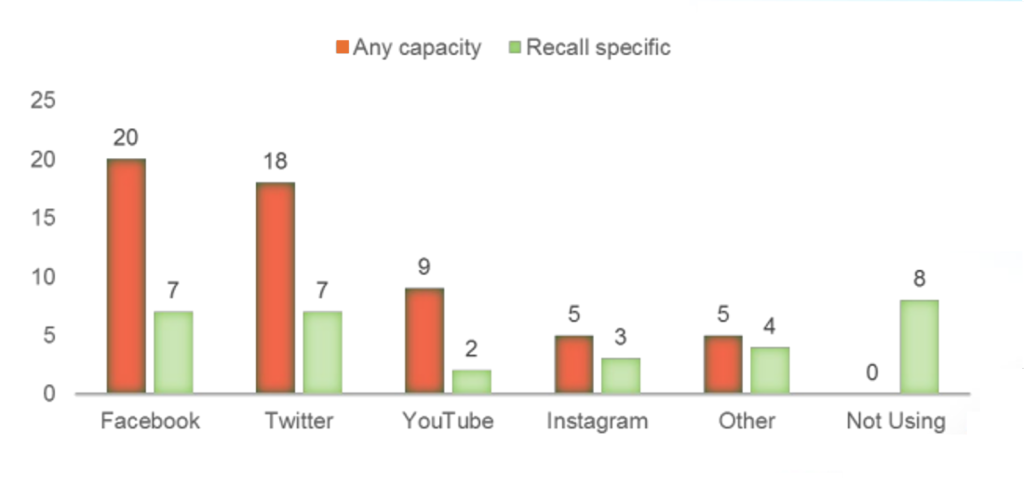
Foodborne Illness Detection – Can Social Media Play Detective?
Foodborne illness outbreaks remain a significant public health concern, affecting millions worldwide. While traditional surveillance methods rely on healthcare data, the potential of social media as a real-time outbreak detection tool is increasingly being recognized.
Large-scale social media data, such as that collected from “X” (formerly Twitter), has shown promise, by aligning with ground truth data reported by the National Outbreak Reporting System (NORS), as illustrated in Figure 2. This demonstrates the potential for social media platforms to potentially allow for earlier detection and faster response to outbreaks [7].
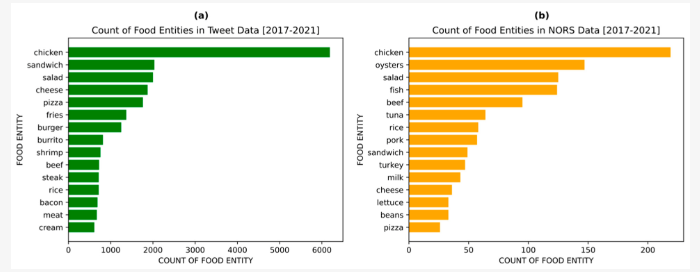
Figure 2: Graph displaying the 15 most frequent food entities found in collected tweets (a) and NORS data (b) from 2017-2021 [7]
Social Media Use – a Positive Impact on Perceived Risk
Perceived risk, shaped by an individual’s understanding of potential negative outcomes, plays a crucial role in consumer choices and food safety practices. Studies suggest a potential link between increased social media use and heightened food safety risk perception, indicating that those who engage more frequently with these platforms may be more attuned to potential hazards.
Social media provide a low-barrier entry point for learning about food safety concerns, Furthermore, social media accessibility, interactivity, and ease of information sharing, all contribute to capturing consumers’ attention and raising awareness about food safety risks [6].
Bridging the Knowledge Gap and Building Trust
Research links social media use with increased trust in science [1], highlighting its potential to foster transparency and trust in the food industry. Open communication channels on platforms like Twitter and Facebook allow producers and regulators to directly engage with consumers, for example, by announcing recalls in real time. This builds trust and shared responsibility for food safety. Additionally, social media provides researchers with valuable data on consumer behaviour, enabling targeted educational interventions [5].
Challenges and Pitfalls
Social media’s unprecedented access to information has the potential to benefit all stakeholders in the food chain, from consumers to producers, experts, and food safety authorities. However, the effective use of social media for sharing food safety information is not without its challenges:
- Diverse Audiences: Tailoring messages to different demographics
- Reliable Data: Filtering and extracting insights from unstructured data
- Data Quality: Combating misinformation and verifying information
- Algorithmic Bias: Social media algorithms can create filter bubbles [9]
Fake Food News
The very features that make social media a powerful communication tool—high engagement and instant two-way communication—also make it vulnerable to the rapid spread of misinformation and disinformation [1]. Anyone can become a self-proclaimed “food expert,” regardless of their credentials. QAssurance’s survey (Figure 3) reveals that many consumers don’t verify the food information they receive, further amplifying the potential harm of false narratives.
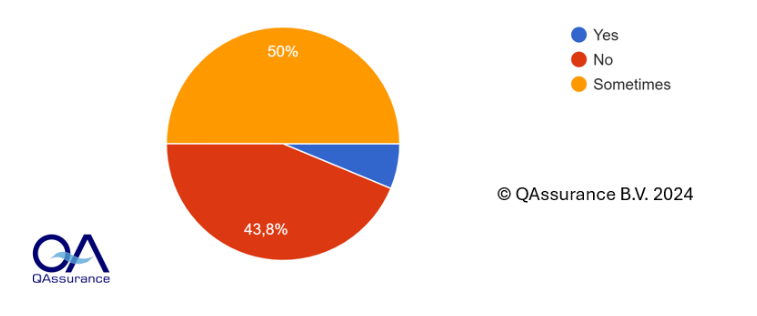
Consequences of Misinformation on Social Media
Consequently, social media becomes a breeding ground for food safety misinformation and disinformation, fueled by anecdotal evidence, false attribution of sources, and the oversimplification of complex topics [1]. The potential harm to food safety manifests in various ways:
- Misleading Information: Unsubstantiated health claims and viral food trends can lead to risky behaviours and delayed healthcare access
- Erosion of Trust: The overload of contradictory information can undermine trust in credible sources
- Unsafe Practices: Influencer endorsements and the allure of trendy ingredients can lead consumers to overlook food safety risks and quality standards [5,6]
Tips for Consumers
To help consumers make informed and safe choices, here’s a list of tips for navigating food safety on social media:
- Think Critically: Verify information from trusted sources before adopting new food trends or recommendations
- Evaluate Endorsements: Research brands and influencers before trusting their advice
- Prioritize Safety: Follow established food safety guidelines when preparing recipes from social media [5]
Implications and Guidelines for Food Safety Stakeholders
A 2023 EFSA study reveals a stark disconnection: 70% of Europeans are interested in food safety, yet 60% find the information too technical [2]. This highlights the need for food safety experts to strategically use social media to bridge this gap. By tailoring their communication to address consumer needs and concerns, experts can foster trust and promote accurate information. Key strategies for effective communication include:
- Strategic Platform Selection: Choose platforms based on audience demographics, content format, and available resources
- Compelling Storytelling: Share personal experiences, anecdotes, and expert insights to engage audiences and build trust
- Proactive Misinformation Management: Actively share reliable information to counter false narratives and address misconceptions
- Social Media Training: Equip experts with the knowledge and skills to communicate effectively on social media platforms [1]
Leading by Example – the Safe4Eat Initiative
In May 2024, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) launched #Safe4Eat, a social media campaign aimed at educating young Europeans (25-45) about food safety and the role of scientists in protecting consumers. The campaign seeks to bridge the gap between scientific expertise and public understanding, empowering individuals to make informed food choices [2].
Is Your Food Company #DigitalReady?
QAssurance is your partner in navigating the complex landscape of digital food safety. We offer a unique blend of consulting expertise and real-time software solutions, like iMIS Food, designed to fortify your food safety infrastructure throughout the entire supply chain. But that’s not it!
We have also developed a “Digital Transformation Calculator” to assess your company‘s digital readiness, pinpointing areas for improvement and providing tailored recommendations. These tools are invaluable for understanding how prepared your business is for the future of digital food safety. By receiving results directly in your email address, you ensure you remain compliant and competitive in an ever-evolving landscape.
Sources
- [1] Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation. (2022). Guideline on Using Social-Media Engagement for Food Safety Risk Communication. In Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation. https://www.apec.org/docs/default-source/publications/2021/12/scsc-01-2020s/guideline-on-using-social-media-engagement.pdf?sfvrsn=9f9d8396_2
- [2] European Food Safety Authority. (2024). “Safe2Eat” 2024 Campaign: empowering consumers across Europe. European Food Safety Authority. https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/safe2eat-2024-campaign-empowering-consumers-across-europe
- [3] Food Safety Magazine. (2024). Hashtags and Hazards: The Dubious Influence of Social-Media Trends on Food Safety. Food Safety Magazine. https://www.food-safety.com/articles/9434-hashtags-and-hazards-the-dubious-influence-of-social-media-trends-on-food-safety
- [4] Ma, J. (2017). Food Safety Information on the Internet: Consumer Media Preferences. https://www.foodprotection.org/files/food-protection-trends/jul-aug-17-ma.pdf
- [5] R, M. (2024). Food Safety for Millennials in Today’s Era of Social Media. Smart Food Safe. https://smartfoodsafe.com/food-safety-through-social-media/
- [6] Safe Food Alliance. (2019). The Role of Social Media in Food Safety and Public Information. https://safefoodalliance.com/food-safety/the-role-of-social-media-in-food-safety-and-public-information/
- [7] Tao, D. (2023). A Novel Foodborne Illness Detection and Web Application Tool Based on Social-Media. Foods, 12(14), 2769. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142769
- [8] USDA. (2021). State of food safety agencies’ use of social media [Presentatieslides]. https://www.usda.gov/sites/default/files/documents/Badour_Jessica_Pres-FINAL.pdf
- [9] Zhang, J. (2022). Effect of social-media use on food safety risk perception through risk characteristics: Exploring a moderated mediation model among people with different levels of science literacy. https://europepmc.org/article/pmc/pmc9562472
Related articles to Food Safety in the Social Media Age - Opportunities and Challenges
Many customers and visitors to this page 'Food Safety in the Social Media Age - Opportunities and Challenges' also viewed the articles and manuals listed below:
